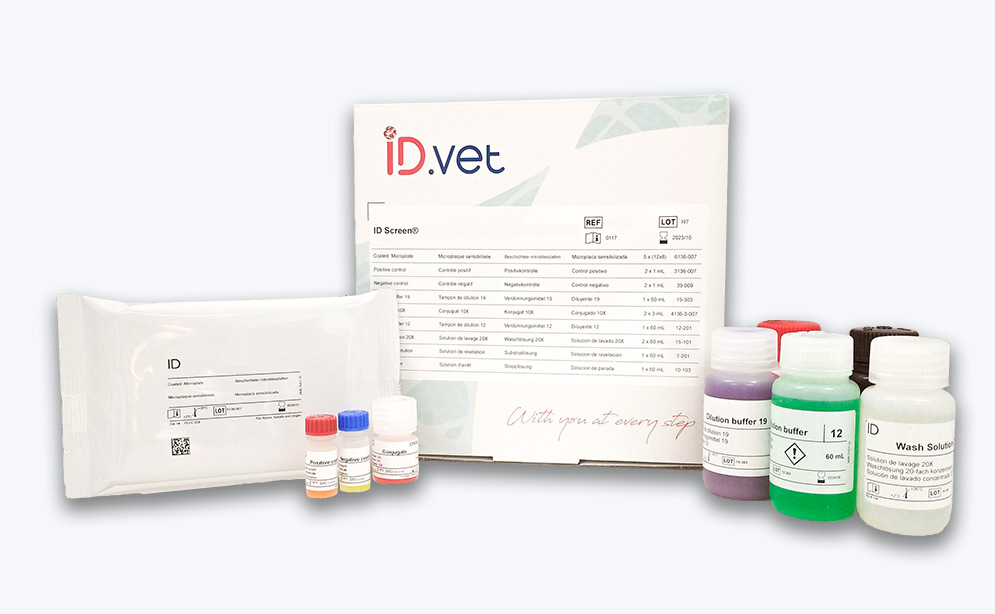
ID Screen® FMD NSP Competition dựa trên cơ chế ELISA cạnh tranh để phát hiện bệnh lở mồm long móng 3ABC thông qua phát hiện protein phi cấu trúc (NSP) của virus trong huyết thanh và huyết tương từ bò, cừu, caprine, lợn và tất cả các loài nhạy cảm
*Lưu ý: Sản phẩm ID Screen® yêu cầu 4 giếng đối chứng cho mỗi lần chạy chứ không phải 6 giếng đối chứng như các ELISA thương mại khác. Do đó, số lượng mẫu tối đa có thể chạy trên mỗi đĩa là 92 chứ không phải 90. Nếu quy trình bao gồm đối chứng dương tính thấp, thì đối chứng này sẽ được cung cấp theo yêu cầu. Vui lòng liên hệ với chúng tôi để biết thêm thông tin.
Ưu điểm nổi trội:
- Độ nhạy và độ đặc hiệu cao
- Thời gian ủ ngắn và qua đêm: khả năng cung cấp kết quả FMD trong cùng ngày khi sử dụng quy trình ngắn
- Dễ sử dụng: không có thuốc thử đông khô và tất cả các dung dịch đệm pha loãng đều được cung cấp ở dạng có màu và sẵn sàng sử dụng
- Phát hiện hiệu quả động vật mang mầm bệnh
- Tiện dụng: bạn có thể dễ dàng kiểm tra xem tất cả các mẫu đã được nạp hay chưa vì dung dịch đệm pha loãng sẽ thay đổi màu sắc khi thêm huyết thanh.
Đặc tính kỹ thuật:
| Thông số |
Nội dung |
| Phương pháp |
ELISA cạnh tranh |
| Loài |
Động vật nhai lại, lợn và tất cả các loài nhạy cảm |
| Nền mẫu |
Huyết thanh và huyết tương |
| Kháng nguyên phủ giếng |
Protein tái tổ hợp 3ABC |
| Kháng thể cộng hợp |
Kháng thể kháng 3ABC NSP lại cộng hợp - HRP (nồng độ 10X) |
Thông tin đóng gói sản phẩm:
| Mã sản phẩm |
Đóng gói |
Số lượng phản ứng |
Dạng đĩa |
| FMDNSPC-5P |
5 đĩa |
480 |
12 x 8 giếng |
| FMDNSPC-10P |
10 đĩa |
960 |
12 x 8 giếng |
Tài liệu trích dẫn:
- OIE Terrestrial Manual 2012; 2.1.5; Foot and mouth disease: http://www.oie.int/fileadmin/Home/eng/Health_standards/tahm/2.01.05_FMD.pdf
LARGE AND SMALL RUMINANTS:
- Browning C. et al. (2020).Inter-laboratory comparison of 2 ELISA kits used for foot-and-mouth disease virus non structural protein serology. Journal of Veterinary Diagnostic Investigation 32.6 (2020): 933-937
- Mesfine M. et al.(2019). Sero-Epidemiology of Foot and Mouth Disease in Domestic Ruminants in Amhara Region, Ethiopia. Front. Vet. Sci. 6:130
SMALL RUMINANTS:
- Albayrak H. et al. (2018). Serological evidence of foot and-mouth disease virus infection in goat breeds in the Samsun province of Turkey. Journal of the Hellenic Veterinary Medical Society, 68(3), 327-330
- Torsson E. et al. (2017). Seroprevalence and risk factors for peste des petits ruminants and selected differential diagnosis in sheep and goats in Tanzania. Infection Ecology & Epidemiology, 7:1368336
- Päärni M. (2016). Seroprevalence of CCPP, FMDV, BTV and BVDV among small ruminants in Tanzania – A minor field study with focus on differential diagnoses of peste des petits ruminants virus. Degree Project in Veterinary Medicine, Clinical Sciences ISSN: 1652-8697 (p21,22,25,26)
LARGE RUMINANTS:
- DEFRA EVID4 Evidence Project Final Report Pirbright Institute (2018). Development and evaluation of improved diagnostic tests for vesicular viral diseases of livestock
- Hemida M. et al. (2018). Foot-and-mouth disease virus O/ME-SA/Ind 2001 lineage outbreak in vaccinated Holstein Friesian cattle in Saudi Arabia in 2016. Veterinary Quarterly, 38:1, 88-98
- Sulayeman M. et al. (2018). Isolation, molecular characterization and sero prevalence study of foot-and-mouth disease virus circulating in Central Ethiopia. BMC Veterinary Research 14: 110
- Babangida D. et al. (2017). Sero survey of foot and mouth disease virus infection in cattle crossing some major border states in Northwestern Nigeria. FOLIA VETERINARIA, 61, 3: 12—18
- Dill V. et al. (2017). Interlaboratory validation of foot and mouth disease diagnostic capability in Germany. Veterinary Microbiology 203, 62-67
- Elnekave E. et al. (2016). The serological response against foot and mouth disease virus elicited by repeated vaccination of dairy cattle. Vaccine 08.054
- Tewari A. et al. (2016). Comparison of two commercial NSP antibody tests (PrioCHECK® and IDvet®FMDV NS ELISAs) to detect infection in vaccinated animals (DIVA). Poster presented at the EuFMD Meeting-Cascais Portugal, Oct 2016
OTHER SPECIES:
- Azizi M. et al. (2017). Serological Detection of Foot and Mouth Disease (FMD) in Camels of South of Iran (Fars, Bushehr and Hormozgan Province). Applied Animal Science Research Journal No 24 pp: 29-34
EMERGENCY SUPPLY:










_22.png)
